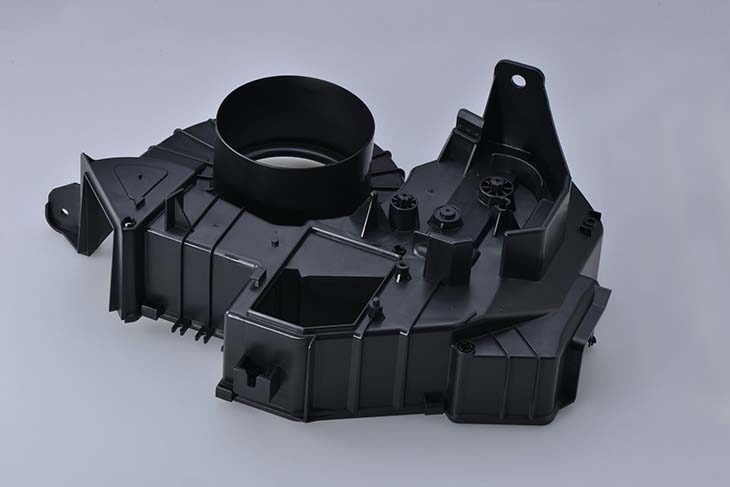
The Ultimate Guide to Injection Molding Processing offers valuable insights into the production of plastic components for various industries, including automotive, home appliances, and medical devices. With the help of injection molding, manufacturers can effectively protect, enhance, and build high-quality products. Injection molding is one of the most common processes utilized in the plastics industry. It enables the production of plastic components in large quantities within a short time span. The process involves the use of different materials such as thermoplastic, thermoset, elastomer, and even metals, allowing for the creation of versatile and high-performance plastics that can withstand high temperatures.
Experienced manufacturers understand the importance of tightly controlled quality throughout the injection molding process. By ensuring precise control over variables, they can guarantee the production of final parts that meet the highest standards. This article delves into the techniques employed by these manufacturers to achieve the best quality plastic components.
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a widely used plastics processing method that involves the injection of heated and liquefied plastic into a temperature-controlled mold under high pressure. The plastic fills the mold and then cools and solidifies to create the finished part or parts. This process is carried out using specialized injection molding machines, also known as IMMs, which come in various sizes and have different mold clamping forces. The production sequence of injection molding involves several steps. Firstly, the mold is closed and the injection "shot" takes place, where the liquefied plastic is injected into the mold cavity. After injection, the mold is kept closed for a period of time known as dwelling, allowing the plastic to cool and solidify. Once the cooling is complete, the mold opens, and the finished products are removed, marking the end of one cycle.
Injection molding is particularly suitable for mass production of molded products with complicated shapes. It is a major process in the area of plastic processing, and its efficiency lies in the execution of these major steps: clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, mold opening, and removal of products. Each cycle can be completed in a relatively short amount of time, enabling high production rates. Specialized hydraulic or electric machines are commonly used in the injection molding process. These machines melt the plastic, inject it into a metal mold, and then set it into the desired shape. The flexibility of mold design and the ability to work with various thermoplastic materials make injection molding a preferred manufacturing process for a wide variety of components. The process is capable of producing complex and highly detailed parts with efficiency.
Set-up and testing of the injection molding process are crucial to ensure consistent quality. Electric injection molding machines are known for their energy efficiency, and the process parameters are tightly controlled to achieve consistent quality across thousands of components produced per hour. This level of consistency and cost-effectiveness is especially beneficial for industries that require injection molded parts and products.
How Does Injection Molding Work?
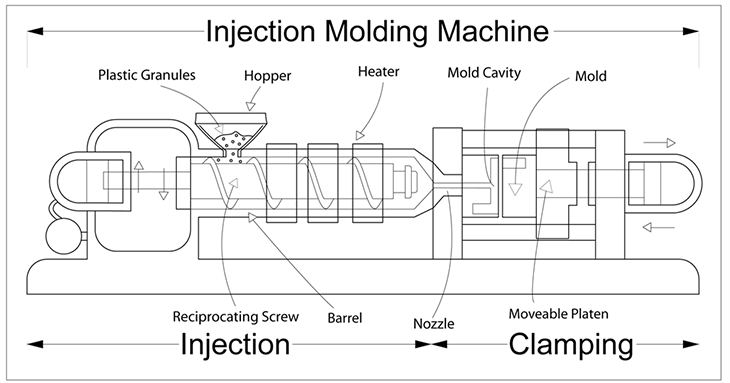
Injection molding is a complex and efficient manufacturing process that produces a wide variety of plastic components. This process involves the use of an injection molding machine, which consists of two primary units: the clamping unit and the injection unit. Each unit plays a critical role in the overall process, ensuring the precise formation of plastic parts.
Clamping Unit: Holding the Mold Securely
The clamping unit of the injection molding machine is responsible for securely holding the mold in place during the manufacturing process. It performs several functions, including the opening and closing of the mold. This allows for easy removal of the finished product once it has been formed. By providing stability and control, the clamping unit ensures consistent and accurate production.
Injection Unit: Melting and Injecting the Plastic
The injection unit of the machine is responsible for melting the plastic material and injecting it into the mold. This unit consists of a hydraulic cylinder, a hopper, and a rotating screw. The process begins with the accumulation of plastic pellets in the hopper, which then move to the front of the machine. The required amount of plastic is metered before being introduced into the injection molding process.
Once the plastic is in a molten state, it is injected into the mold through the rotation and forward movement of the screw. This injection process is carefully controlled, with adjustments made to the speed and pressure to achieve the desired results. The molten plastic fills the cavities in the mold, taking the shape and form of the final component.
Mold Design and Material Selection: Crucial Factors for Quality
The mold itself is a crucial element in the injection molding process. It determines the shape and structure of the final components. Mold design takes into account various factors, such as the types of plastics used and their interaction with the mold. Manufacturers carefully select the appropriate thermoplastic material based on its properties, including ordered molecular structure, semi-crystalline or amorphous nature, and specific characteristics like electrical properties or resistance to high pressures.
Choosing the right thermoplastic material and mold design ensures the overall quality and consistency of the plastic components. Common thermoplastics used in injection molding include Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS), Nylons (PA), Polycarbonate (PC), and Polypropylene (PP). Manufacturers carefully evaluate the requirements of the final component and select the suitable thermoplastic material and mold tool to achieve the desired outcomes.
From Prototype to Production: Ensuring Precision
The development of mold tools is a crucial and meticulous process in injection molding. It often involves using computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D printing technology to digitally develop and validate prototype molds. This approach allows manufacturers to test the molds before committing to the expensive and time-consuming process of developing final bespoke molds.
Once the mold tools are ready, the injection molding machine is set up with the chosen thermoplastic material. The feeding, melting, and injection processes are carefully controlled to ensure accurate and precise formation of the plastic part. The hydraulics and electrical systems of the machine work together to facilitate the feeding and melting of the raw plastic pellets, while the injection screw ensures the smooth flow of molten plastic into the mold.
Precision and Control: Key Factors in the Injection Molding Process
During the injection stage, the pressure is carefully controlled to achieve complete filling of the mold cavities without any plastic escaping. The injection pressure and clamp pressure are adjusted to ensure the right balance, allowing the part to form correctly. Once the desired pressure is reached, the gate opens, and the screw moves forward, enabling the molten plastic to fill the mold precisely.
After the injection, the mold holds the molten plastic for a specific cooling time, allowing it to solidify and take its final shape. The cooling time varies depending on the complexity of the thermoplastic and the component being produced. Once the cooling time is complete, the component is ejected from the mold.
Finishing Touches: Quality Assurance and Distribution
The ejected components undergo finishing processes to ensure their quality and aesthetics. These processes may involve holding and cooling times, as well as additional steps such as polishing, dying, and removing any excess plastic or spurs. Skilled operators carefully monitor and control these finishing processes to achieve the desired final product.
Once the components pass the quality assurance tests, they are inspected, packed up, and prepared for distribution to manufacturers or end-users. Injection molding enables the production of high-quality plastic components with consistency and precision, making it a vital process in various industries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, injection molding is a sophisticated manufacturing process that relies on the interaction between an injection molding machine, mold design, thermoplastic material selection, and precise control of various parameters. By combining these elements, manufacturers can produce a wide range of plastic components efficiently and with excellent quality.
FAQs.
What are the steps in injection molding machine process?
The steps in the injection molding machine process include clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, mold opening, and removal of products. This process involves major steps that are crucial for successful injection molding.
How does the injection molding process work?
The injection molding process works by heating and injecting plastic material under pressure into a closed metal mold tool. The molten plastic then cools and hardens, taking the shape inside the mold tool. Subsequently, the mold tool opens, allowing the molded products to be ejected or removed for inspection, delivery, or secondary operations.
What are the basics of injection molding machine?
The basics of an injection molding machine include the following components: injection molding machines (also known as presses), a material hopper, an injection ram or screw-type plunger, and a heating unit. Molds are clamped to the platen of the molding machine, and the plastic material is injected into the mold through the sprue orifice. These components and the process of injecting plastic into molds form the fundamental elements of an injection molding machine.
Is injection molding a fast process?
Yes, injection moulding is generally considered a fast process. It has the capability to produce an incredible amount of parts per hour, and the speed of production depends on the complexity and size of the mould. The cycle time for injection moulding can range anywhere between 15 to 120 seconds, making it an efficient and time-saving manufacturing method.