Kimla Company, known for its innovation and technological superiority, sets the standards in the industry of advanced CNC machine tools. Since its inception in 1998, Przemysław Kimla’s company has dynamically evolved, moving from the production of control systems to the creation of an impressive range of its own, efficient machine tools. Today, with over 25 years of market experience and having accomplished over 4000 global installations, Kimla embodies the perfect blend of engineering precision, technological innovation, and reliability.
In this interview, we have the pleasure of hosting Mr. Przemysław Kimla, the President of the Board and Owner of Kimla, who shares with us the fascinating story of the brand’s transformation from a local leader in the CNC machine tool industry into a global innovator. The conversation paints a picture of a company continuously pushing the boundaries of technology, from its role as a pioneer in the production of advanced control systems to the introduction of groundbreaking solutions in the field of linear drives and CAD/CAM system integration. Mr. Kimla also describes the strategic directions for the company’s development, its expansion in international markets, and the application of CNC machines in various industries. Insight into the company’s values, its plans for further innovations, and its role in shaping the future of CNC technology provides an inspiring image of a dynamically growing organization that, with passion and commitment, is making its mark in modern industry.
How did Kimla evolve from producing CNC control systems to manufacturing its own advanced machine tools? What were the key turning points in this transformation?
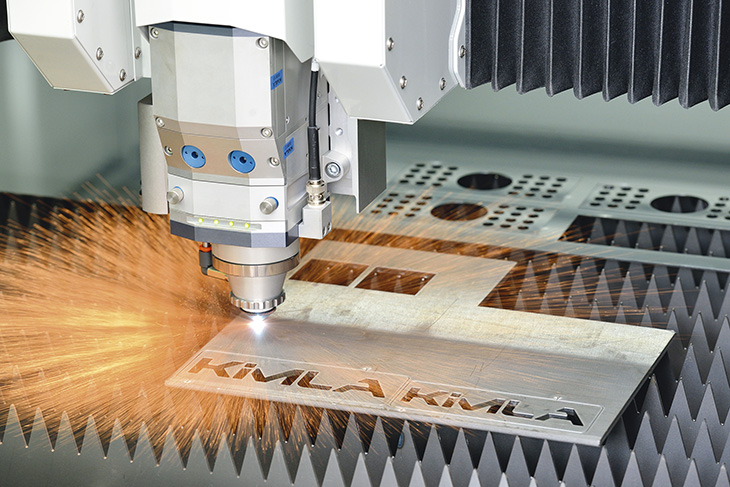
The first CNC machines produced by Kimla, based on its proprietary control systems, were routers, which are large-format CNC milling machines used for cutting materials in sheet form such as wood, plastics, or composites. Such machines were initially used in furniture production or for creating illuminated advertisements. However, due to their robustness and efficiency, they began to be utilized in the aviation industry for milling aluminum and even steel. The next step was the start of waterjet cutter production - machines used for cutting thick metals, glass, stone, or ceramics. The most significant breakthrough, however, was the commencement of fiber laser cutter production, which began somewhat accidentally. When fiber laser sources appeared on the market, there were no popular control systems fast enough to fully exploit the potential of fiber lasers. Available control systems could be fast or precise, but fiber lasers required systems that were both fast and accurate. Kimla was the only company with a control system based on technology that allowed achieving immense working feed speeds without losing the accuracy of the reproduced geometry. To further utilize the potential of fiber lasers, a different type of axis drive was also necessary, as commonly used gear rack drives were too slow, not accurate enough, and wore out quickly due to friction and frequent load changes. Magnetic linear drives, already known to be much faster, more accurate, and wear-free because they operate contact-free, were the perfect solution. However, they were very expensive, leading many laser manufacturers to avoid using them. Kimla, as the sole laser cutter manufacturer, began producing its own linear drives. After optimizing the production process and bypassing intermediaries, it became possible to offer a very fast machine with linear drives at an attractive price. Currently, Kimla is the sales leader of laser cutters in Poland and is dynamically expanding its sales abroad. In addition to the mentioned machines, we are dynamically developing the production of cutters, machines for oscillating knife cutting of textiles, foams, rubbers, or insulating materials. Here, we earned success with an exceptionally strong oscillating head, in which we used two servo drives, one for setting the angle of the knife and another for oscillation. The power of such a drive is often ten times greater than in competing machines, allowing for cutting materials for reinforced gaskets with mesh and sheet metal.
Could you specify what particular technological innovations you have introduced in the CNC machining industry that set you apart from the competition?
Since Kimla produces its own linear drives, they have become the hallmark of our company. As the sole company, we began mass production of routers with linear drives, which translates into a significant increase in accuracy. For instance, in standard routers, the backlash in gear drives is 0.05mm, limiting their accuracy to that value. Kimla machines with linear drives can move to 0.001mm without any backlash, indicating that these machines are 50 times more accurate than other competitive devices. As a result, they are unparalleled in many applications.
What are the main types of machine tools produced by KIMLA, and what are their unique features?
Routers – Machines with an exceptionally heavy, solid, and rigid construction. Most machines of this type typically weigh around 2 tons, whereas a similar Kimla machine weighs about 6 tons. Combined with linear drives, they are much faster and more accurate, and due to their rigidity, they even allow the use of milling heads, which is impossible for similar machines.
Lasers – The fastest fiber laser cutters. In some cases, one Kimla cutter replaced 5 other fiber cutters. These machines also have the lowest operating costs, mainly due to Kimla’s service policy.
Waterjets – When the capabilities of lasers end, the potential of waterjet cutters begins. These machines cut almost any material of any thickness, making them an excellent complement to lasers.
Cutters – Machines designed for cutting packaging, fabrics, foams, gaskets, and insulating materials.
Tool milling machines – Kimla offers three- and five-axis CNC milling machines with linear drives, which are characterized by exceptional accuracy and efficiency.
How have your proprietary solutions in linear drives and control systems impacted the efficiency and precision of the machines produced?
Magnetic linear drives are a technology that should soon replace all other types of axis drives in CNC machines. Currently, only about 1% of CNC machines worldwide are equipped with these types of drives, and their low popularity is due to their high cost. They are used exclusively in very demanding applications where they cannot be replaced with cheaper solutions. However, their high price mainly results from the small scale of production, and as their popularity increases, the prices of machines with linear drives should decrease. Often, machines with linear drives were twice as expensive as machines with traditional drives. At Kimla, machines with linear drives cost as much as other companies’ machines with traditional drives, which translates into their high popularity, as customers get a much better machine for the same price.
How do you develop and integrate software with the CNC machines you manufacture?
Previously, all CNC machines were programmed in a very inconvenient way. Initially, a designer had to design a part in CAD software, then a technologist often had to generate the technology at another station using CAM software, and the program saved in G-code was then sent to the operator, who loaded the program into the machine and started the machining process. This is particularly noticeable with laser cutters, where the cutting process of a part can take 5 seconds, but the preparatory activities take half an hour. Such a process unnecessarily wastes the time and labor of many people. In today’s times, this can be significantly improved. Kimla was the first to integrate CAD, CAM, nesting, and CNC modules into the control system, allowing all preparatory activities to be performed by one person. Also, any corrections to existing programs can be made within a few seconds directly on the machine.
Could you describe the most challenging and technically advanced projects you have implemented?
Undoubtedly, the most important project is the comprehensive development of the company in all aspects collectively called mechatronics, which includes mechanics, electronics, and software. Only the combination of these three fields of technology yields above-average results. In addition to the aforementioned linear drives, Kimla manufactures its own laser cutting heads in which it has implemented many patented technologies. Among others, a magnetic lens drive and direct temperature measurement of lenses and fiber optics using thermal imaging cameras. This provides exceptional control and allows for continuous diagnostics of the optical state.
What are your plans for development and expansion, both in domestic and international markets?
In the Polish market, Kimla is a leader in all fields of its activity. Abroad, the largest market is the UK, which is challenging, but thanks to a good distributor, we have been increasing our share in that market for many years, where several hundred of our machines are already installed. Apart from the UK, we have quite a few installations in all the countries neighbouring Poland. However, Europe is not everything. We are currently intensively developing distribution in the USA and Canada, where the market is comparable to the whole of Europe. Among the more exotic destinations, we can mention Brazil, Egypt, South Africa, Israel, New Zealand, Australia, and Ghana.
In which industries are machines with the Kimla logo used, and who is your main customer?
Kimla provides CNC machines to a very diverse range of industries. Starting from the advertising industry, through the metal industry, aviation, services, to the defence industry and automotive. Companies such as Tesla, LG-chem, Siemens, Bosch, Volkswagen, ABB, and Beko work on Kimla machines.
What are the key partnerships and collaborations that have helped you develop and maintain your position in the market?
Kimla is largely self-sufficient; we produce our own control systems, electronics, software, machine bodies, and laser heads, but there are also many components that we purchase. We try to use the highest quality components without compromise. Our suppliers include companies like IPG, HSD, Igus, Gudel, Hypertherm, Becker, and Bosch. Close cooperation with suppliers is very important to improve the supplied components also based on user experiences.
What does your team look like, and what values are most important to you in team management?
In a technology company, the research and development department plays a significant role. As many solutions used in our machines were developed in-house, we have been dynamically developing this department for many years. A dedicated team of scientists works in the dedicated “Kimla labs” building, where research and development of modern innovative technologies are conducted. This is where our control systems, linear drives, and laser heads are created. The laboratory is equipped with the most modern research equipment and clean rooms for working with the most precise components.
What social and ecological initiatives does Kimla undertake?
Our company cooperates with schools and universities where students undertake internships and apprenticeships. It is an excellent way to recruit employees, as we have acquired many talents in this way. Together with universities, we also conduct research projects to utilize their academic achievements while allowing students to write their master’s and doctoral theses based on research conducted in our company.
What are the biggest technological and market challenges facing the company?
We have never lacked ideas for new devices or technologies, and the main limitation is the time for their development. In today’s times, market expectations are dynamically changing, and it is necessary to quickly respond to emerging needs. The philosophy of our company has always been the modularity of the machines produced, allowing us to relatively easily build subsequent devices based on already produced components, significantly shortening the time to market.
What are your company’s strategic goals and visions for the future?
Seeing the huge needs of the CNC machine market and the permanent sales limitations by production capabilities, Kimla decided to build a new factory, which is already at an advanced stage, and we plan to start production later this year. Currently, one CNC machine is produced per day. The new factory has 25,000m2 of production space and 4,800m2 of office and administrative space. Thanks to this, the production capabilities of Kimla will increase fourfold, and the production of laser cutters alone will increase to one per day.
How do you see the future of CNC technology and your role in its evolution?
The world is developing at an increasingly rapid pace, and the lifespan of products is shortening. This means that traditional mass production methods such as plastic forming are becoming less economical and are being replaced by production that does not require the preparation of very expensive tools. CNC machines can perform equally well whether producing 1,000 units or a single unit, which perfectly fits into the custom needs of an increasingly affluent society. I believe that the CNC machine industry will continue to develop at a rapid pace for many years to come, as digital technologies are taking over more and more areas of life and production.