3D metal printing has rapidly evolved from a niche prototyping tool to a foundation of modern manufacturing, revolutionizing how organizations design and produce products. Initially focused on creating small-scale, intricate objects, this technology now allows the production of large, complex components across aerospace, automotive and medical fields.
Manufacturers eagerly anticipate new developments in 3D metal printing, which promise to enhance production speed, reduce costs and enable the creation of designs previously impossible to achieve. These advancements hold the potential to set new industry standards, urge professionals to stay abreast of the technology’s progression, and integrate its groundbreaking capabilities into their manufacturing processes.
Innovations in Printing Technology
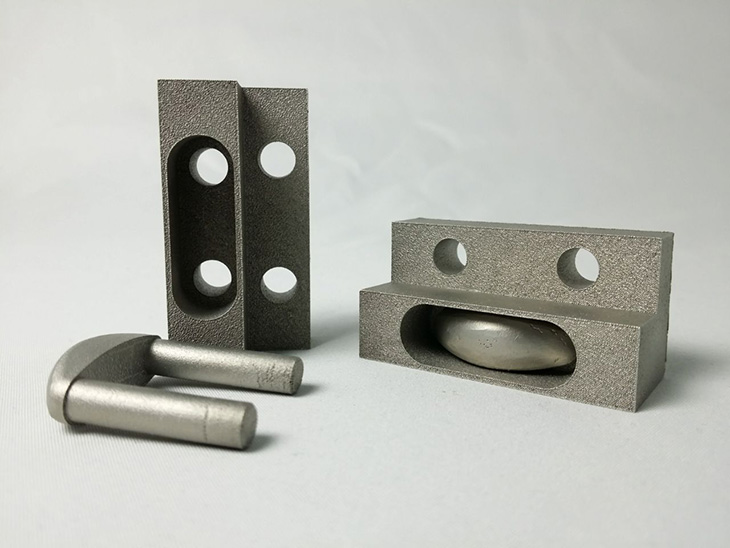
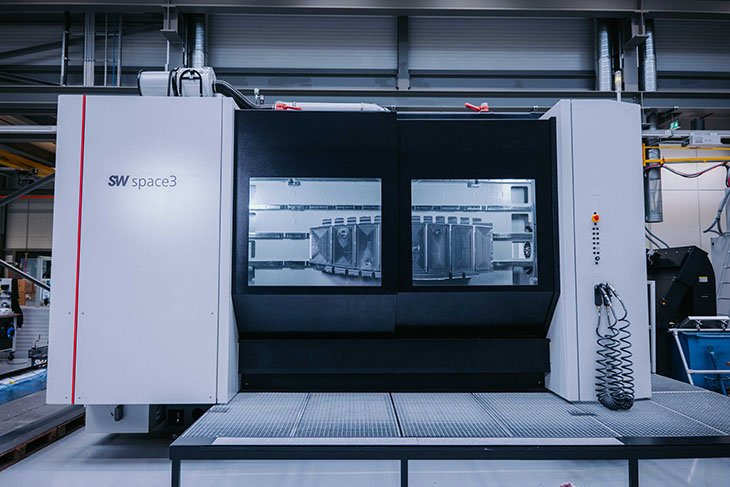
The latest 3D metal printers showcase remarkable speed, precision and scalability advancements. They transform the manufacturing industry with their ability to produce high-quality parts faster and more accurately than ever.
These state-of-the-art machines — with cutting-edge technology — support using recycled materials. They significantly lower the environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and reducing reliance on virgin raw materials.
This eco-friendly approach mitigates the environmental footprint, slashes production costs and minimizes material waste while boosting production efficiency. Manufacturers now reap the benefits of these innovations — which facilitate the creation of more sustainable, cost-effective and high-quality products — setting a new standard in the competitive manufacturing industry.
Advancements in Printing Materials
Recent advancements in metal alloys — including enhanced strength, durability and lightweight properties — are pushing the boundaries of 3D metal printing applications. These innovative materials — like titanium, aluminum and nickel-based superalloys — can withstand the demanding environments of aerospace, automotive and medical industries.
Their exceptional performance under stress and in extreme temperatures makes them ideal for producing complex, high-performance parts. For the aerospace industry, these alloys contribute to lighter, more fuel-efficient aircraft. In automotive manufacturing, they enable the creation of durable, lightweight components that improve vehicle efficiency and safety.
Meanwhile, in the medical sector, their biocompatibility and strength support the production of personalized implants and devices. This expansion of 3D metal printing applications underscores the technology’s versatility and potential to revolutionize traditional manufacturing processes with custom, high-quality solutions.
Improved Software and Design Tools
The advent of advanced software solutions in 3D metal printing has opened new avenues for creating more complex designs with unprecedented precision. These digital tools, with the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning — refine printing processes and optimize material usage. AI algorithms analyze design parameters and printing conditions in real time to adjust processes and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
Despite these advancements, the emphasis on rigorous quality control remains paramount. This commitment to excellence enables manufacturers to reduce waste, cut costs, elevate efficiency and foresee and rectify potential production challenges. Integrating these smart software solutions ensures each printed component meets the high standards required to solidify 3D metal printing’s role as a transformative force in modern manufacturing.
Training and Skill Development for the Future Workforce
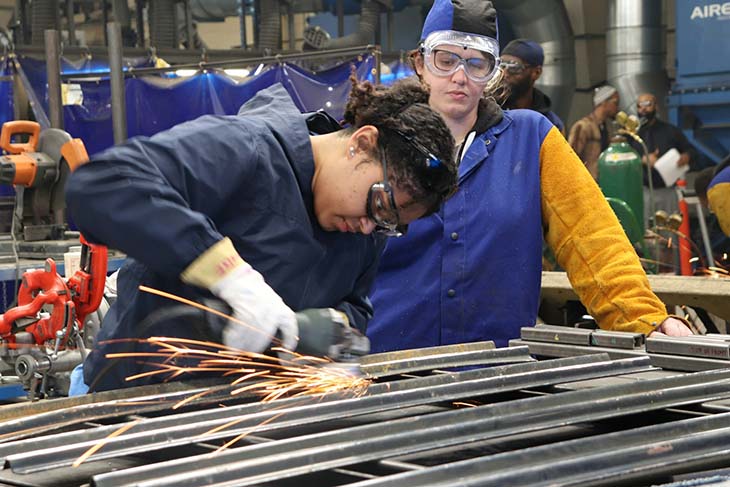
The manufacturing industry faces the daunting task of filling at least 4 million jobs by 2030. This number underscores the need for specialized training programs in advanced 3D printing technologies. A collaborative effort between tech companies and educational institutions is essential to bridge this gap in developing comprehensive courses and certifications.
These programs equip the workforce with the necessary skills to operate sophisticated printing machinery, emphasizing the technical aspects, creativity and problem-solving in manufacturing processes. Such partnerships are pivotal in cultivating a talent pool that meets the industry’s demand. It guarantees the workforce is prepared to leverage the full potential of 3D metal printing in enhancing production capabilities and innovations.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite promising advancements in the practice, this technology faces limitations, notably cost and accessibility. High initial investment for advanced printers and materials remains a barrier for many smaller manufacturers. However, ongoing research vigorously addresses these challenges and focuses on making 3D printing more cost-effective and widely accessible. Thus, innovations that can reduce material waste and enhance printer efficiency are pivotal.
Meanwhile, experts are optimistic and project the global 3D printing products and services market could surge to over $37 billion by 2026. This growth comes with continuous improvements in printing technologies and a broadening acceptance of printed components across industries. As the technology becomes more mainstream, its adoption can further reduce costs and open new opportunities for innovation and customization in manufacturing.
Innovations in Manufacturing With 3D Metal Printing
Manufacturing professionals must stay abreast of the latest advancements in 3D metal printing, as these innovations are vital to transforming production processes, enhancing efficiency and driving down costs. Exploring and integrating these cutting-edge technologies into their operations unlocks innovations and competitive advantage in the evolving manufacturing sector.